Introduction
Ulceration esophagus or Esophageal Ulcer is a complex and often misunderstood condition that significantly affects your digestive health. Open sores or lesions in the esophageal lining appear as a result of different underlying causes leading to a spectrum of uncomfortable symptoms.
Loub that connects the mouth to the stomach through its muscular structure serves as a vital conduit for both food and liquid through the body. Any compromise to its lining—such as that seen in ulceration esophagus—can lead to serious complications if not promptly and properly managed.
Further Reading:
Abdominal Pain & Headache: When to Worry and How to Relieve It
Pain in Abdomen with Constipation: 7 Signs, Causes, and How to Get Back on Track
What Is Ulceration Esophagus?
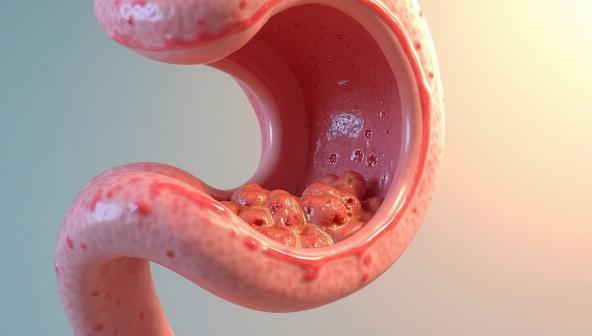
It refers to the development of ulcers in the esophageal mucosa—the innermost lining of the esophagus. The affected area in Esophageal Ulcer develops from persistent inflammatory conditions or from continuous tissue irritation and exhibits different ranges of dimensions and disease intensity.
Understanding the Esophageal Mucosa
The mucosa works as a protective soft tissue layer which shields the esophagus against both friction and small injuries. The lining of the esophagus can develop ulcers when exposed to harmful substances or acid reflux on multiple occasions.
The Key Characteristics
- Lesions or open sores in the esophagus
- Inflammation and tissue damage
- Potential for infection or bleeding
- The condition develops because of GERD or infections together with other underlying medical conditions.
- It can be both acute and chronic, and its recurrence is common without proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
The Common Causes
Identifying the root cause of ulceration esophagus is crucial to developing an effective treatment plan. Several different causes exist which lead to ulcer formation in the esophageal lining.
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Stomach acid that frequently returns to the esophagus during GERD damages the mucosa until it forms ulcers because of repeated exposure. Chronic acid exposure is the leading risk factor for ulceration esophagus.
2. Medication-Induced Esophagitis
Medications sometimes create two problems for the esophageal lining by directly causing irritation and acid production that results in ulcers. Common culprits include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Antibiotics like doxycycline or tetracycline
- Bisphosphonates used for osteoporosis
- Potassium chloride tablets
3. Infections
People with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to infections that can cause ulceration esophagus. These include:
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Candida albicans (fungal infection)
4. Radiation Therapy
The treatment of cancer through chest or neck or upper abdominal radiation therapy results in esophageal damage that causes ulcer formation.
5. Ingested Irritants
Consuming dangerous substances such as bleach, lye and sharp objects leads to instant severe ulceration of the esophagus because of direct injury.
6. Excessive Alcohol and Tobacco Use
Smoking together with alcohol consumption creates a double risk factor because these substances simultaneously damage the esophageal mucosa and boost acid production and decrease healing time which leads to ulcer development.
Risk Factors for Ulceration Esophagus
Certain individuals are more prone to developing ulceration esophagus due to lifestyle, genetic, and health-related factors.
- Chronic GERD or heartburn
- Immunocompromised status (HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy)
- Regular use of irritating medications
- Heavy smoking or alcohol use
- History of esophageal trauma or surgery
Your current risk status enables you to make better prevention choices as well as access medical care at the earliest opportunity.
Symptoms of Ulceration Esophagus
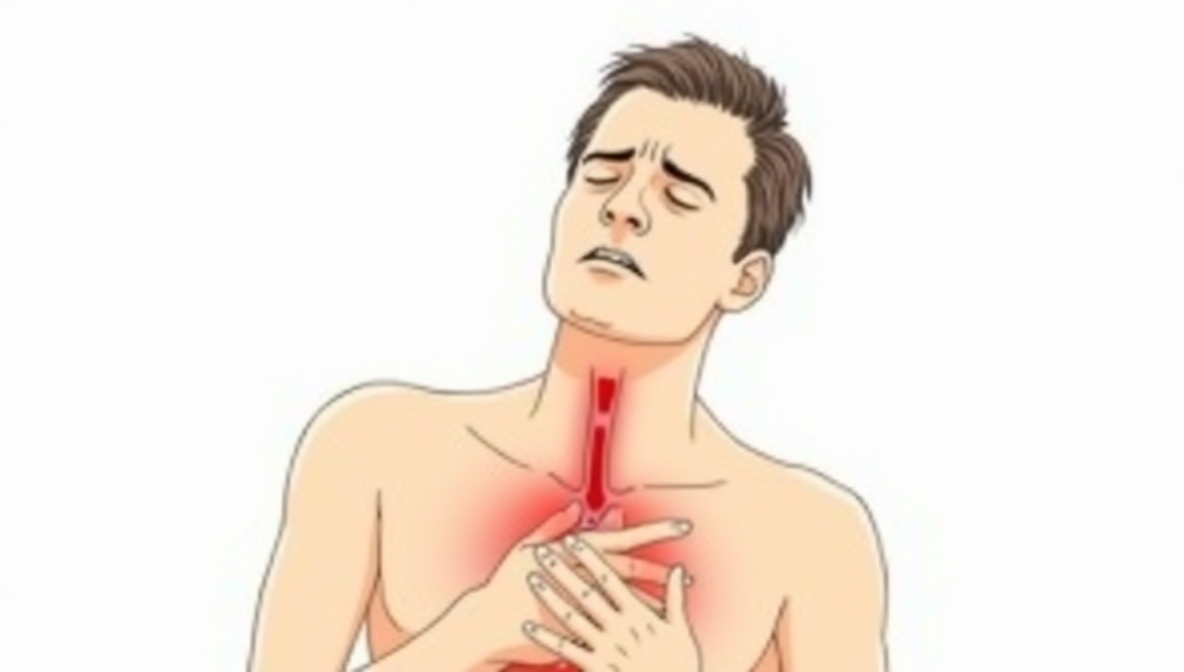
Recognizing the symptoms of ulceration esophagus can help in prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms
- People with ulcerative esophagitis experience burning sensations or chest pain.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Painful swallowing (odynophagia)
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Unexplained weight loss
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
- Chronic sore throat or hoarseness
- Patients can experience vomiting that contains blood alongside black tarry stool which indicates bleeding ulcers.
Advanced Symptoms
If left untreated, ulceration esophagus can lead to more severe and persistent symptoms, such as persistent coughing, anemia, or signs of esophageal perforation.
How Ulceration Esophagus Is Diagnosed
Timely and accurate diagnosis is critical to managing ulceration esophagus effectively.
1. Endoscopy
Doctors use endoscopy as the primary method to detect esophageal ulcers. The diagnostic method involves using an instrument that combines a tube with a camera to view the esophageal walls.
2. Biopsy
Treatment through endoscopy involves extracting tissue specimens for examination by histology to find and eliminate cancer and infections besides other possible medical conditions.
3. Imaging Studies
Barium swallow provides essential information about structural problems within the body.
CT scans help identify perforations which are potential complications of the condition.
4. Laboratory Tests
- Medical staff conduct blood tests to determine whether anemia or infection exists.
- Swab tests of tissue specimens will be conducted to identify infectious causes.
Medical Treatment for Ulceration Esophagus
The treatment plan for Esophageal Ulcer depends on its underlying cause, severity, and patient history.
Pharmacological Interventions
- Omeprazole together with esomeprazole and other Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) help decrease acid production in the stomach.
- H2 Receptor Blockers: Ranitidine, famotidine for milder cases
- Sucralfate: Forms a protective coating over the ulcer
- Antacids: Provide quick but temporary relief
- Antibiotics/Antivirals/Antifungals: If infection is identified
Surgical Treatment
- Medical staff perform surgery exclusively for severe cases that resist other treatments or develop perforations or strictures.
- Fundoplication: Strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter
- Esophageal dilation: For strictures
- Extremely severe cases may require performing an esophagectomy where doctors remove part of the esophageal tissue.
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes

In conjunction with medical treatments, lifestyle modifications are essential in managing and preventing ulceration esophagus.
Foods to Avoid
- Spicy and acidic foods
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Tomatoes and tomato-based sauces
- Chocolate and peppermint
- Caffeinated drinks and carbonated beverages
- Alcohol
Foods to Include
- Non-citrus fruits like bananas and melons
- Oatmeal and whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Cooked vegetables
- Herbal teas (e.g., chamomile, ginger)
Helpful Habits
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoid eating 2-3 hours before bedtime
- Elevate the head of the bed
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing
- Smokers should stop their habit while drinking alcohol in moderation
The Complications
If not properly managed, ulceration esophagus can lead to several serious health issues.
Major Complications
- Esophageal Strictures: Narrowing due to scar tissue
- Perforation demands emergency surgical intervention because it represents a life-threatening condition.
- Bleeding ulcers from ulceration esophagus create the risk of severe anemia or fatal blood loss.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: Precursor to esophageal cancer
- Esophageal Cancer: Particularly adenocarcinoma
Prognosis and Long-Term Management

Can Ulceration Esophagus Be Cured?
With prompt and effective treatment, most cases of Esophageal Ulcer can be resolved. The condition tends to come back frequently since treating the original cause (GERD) remains essential for prevention.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Regular endoscopic evaluations
- Adjusting medication as necessary
- Medical testing of blood helps physicians detect complications during patient care.
Support and Counseling
Dealing with a chronic condition like ulceration esophagus can be emotionally taxing. Your care plan would benefit from the addition of support groups and dietary counseling as well as mental health services.
Conclusion
Ulceration esophagus is more than just a painful condition; it’s a signal that something deeper is amiss in your digestive health. The necessity to detect Esophageal Ulcer quickly becomes vital since it creates major health difficulties. Knowing the factors behind ulceration esophagus enables you to grasp your health better so you can take active control.
Patients can achieve lasting relief together with exceptional life quality through proper treatment. Patients who want successful management of this condition must perform regular follow-ups with doctors while staying vigilant about symptoms while maintaining constant health care efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of ulceration esophagus?
The primary symptoms of this consist of chest pain combined with difficulty swallowing and painful swallowing as well as regurgitation.
Can ulceration esophagus be life-threatening?
The condition becomes a medical emergency whenever bleeding or perforation develops.
How long does it take to heal?
The healing process requires several weeks to a few months based on treatment compliance together with the extent of injury.
Is surgery always required?
The majority of Esophageal Ulcer cases receive medical treatments. Medical professionals use surgery only for treating complications or cases that do not respond to medical treatments.
Are there natural remedies for ulceration esophagus?
The pain-relieving effects of chamomile tea or slippery elm cannot substitute proper medical treatment for Esophageal Ulcer.
Can children develop ulceration esophagus?
Children with GERD along with those who have weakened immune systems are at risk for developing ulcers but the condition mainly affects adults.
https://shorturl.fm/PDniU
https://shorturl.fm/TjFhe
https://shorturl.fm/qIJPM
https://shorturl.fm/23pUf
https://shorturl.fm/MBKfV
https://shorturl.fm/pe343
https://shorturl.fm/74UqD
https://shorturl.fm/e2174
https://shorturl.fm/BJVXL
https://shorturl.fm/n17eT
https://shorturl.fm/QBH3C
https://shorturl.fm/JzQNx
https://shorturl.fm/iAN1m
https://shorturl.fm/12R0p
https://shorturl.fm/bSVCh
https://shorturl.fm/CXvi1
https://shorturl.fm/CXMY1
https://shorturl.fm/9fzNd
https://shorturl.fm/cBQBN
https://shorturl.fm/SKXGI
https://shorturl.fm/smPkY